Experiencing a Heavy Period? It Could be Underlying Health Issues
Updated August 19, 2025

Written by Dr Barak Lilian, intern in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Israel
Heavy periods, also known as menorrhagia, refer to menstrual bleeding that is abnormally heavy or prolonged. While every woman's menstrual cycle is unique, heavy periods can significantly affect the quality of life and may be indicative of underlying health issues. Understanding the potential causes and possible treatments for heavy periods can help maintain menstrual health and improve quality of life.
Causes of heavy periods may include:
- Hormonal imbalances: Irregularities in estrogen and progesterone levels can cause the endometrium (uterine lining) to overdevelop, leading to heavier bleeding.
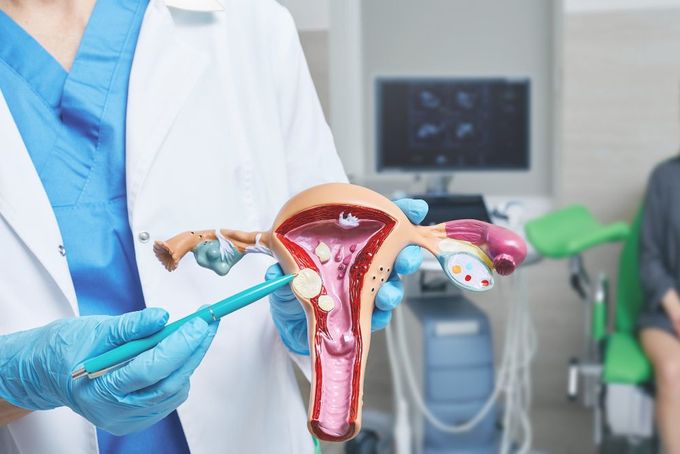
- Uterine fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus can lead to heavy or prolonged periods.
- Polyps: Small, benign (non-cancerous) growths on the uterine lining can cause heavy bleeding.
- Adenomyosis: Endometrial tissue grows into the uterine muscle, leading to painful and heavy periods.
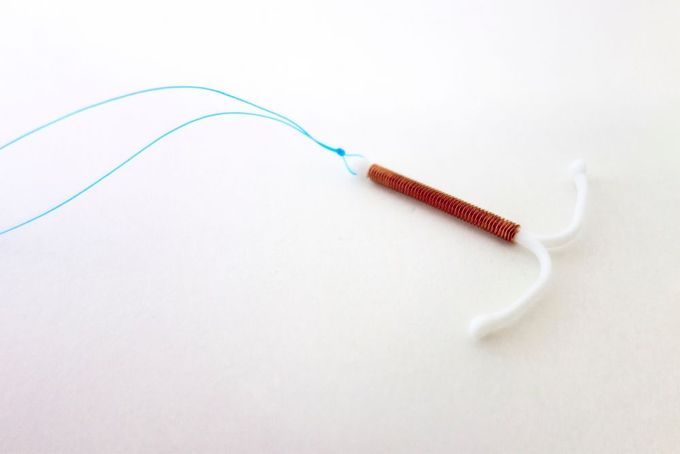
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs): Some women may experience heavy or irregular periods after insertion of a non-hormonal IUD.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This is an infection of the female reproductive organs that can cause heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition where the endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, causing painful and heavy periods.
- Bleeding disorders: Conditions such as coagulation disorders can cause excessive menstrual bleeding.
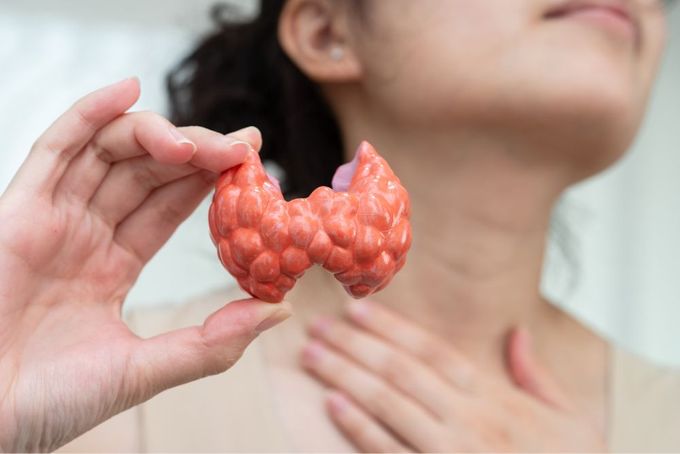
- Hormonal: Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, is when the thyroid gland doesn't make enough thyroid hormones to meet your body's needs, and can cause heavy bleeding.
- Certain medications: Blood thinners and aspirin may cause heavy periods.
- Uterine or cervical cancer: Although rare and more common in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women with risk factors, these cancers can cause heavy bleeding.
Treatment for heavy periods depends on:
- The underlying cause
- The severity of the bleeding
- Overall health
- Your personal desire for a degree of intervention
Some possible treatment options include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help reduce menstrual bleeding and alleviate pain.
- Tranexamic acid: This is a prescription medication that helps reduce menstrual blood loss.
- Surgical interventions: In cases where medication is ineffective, you should consult your physician about surgical options. There is a wide range of surgical therapies, ranging from endometrial ablation, uterine artery embolization, myomectomy, or even hysterectomy. Each therapy has its own pro and cons, and should take into consideration to your age, medical background, and desire for intervention.
- Iron supplements: After evaluating and treating the underlying cause of menorrhagia, iron supplements can help restore iron levels and treat anaemia.
- You can also look to natural options to support your health, such as balancing histamine levels, abdominal massage, Epsom salts, heat packs or tens machines, such as Myoovi.
Always consult your medical practitioner when reviewing your treatment options. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve overall menstrual health.